What is forging ?
Forging refers to the process of shaping metal (or other materials) by heating it to a high temperature and then hammering or pressing it into the desired shape. The process of forging is typically used to create strong and durable objects, such as tools, weapons, and machine parts. The metal is heated until it becomes soft and malleable, and then it is placed on an anvil and shaped using a hammer or press.
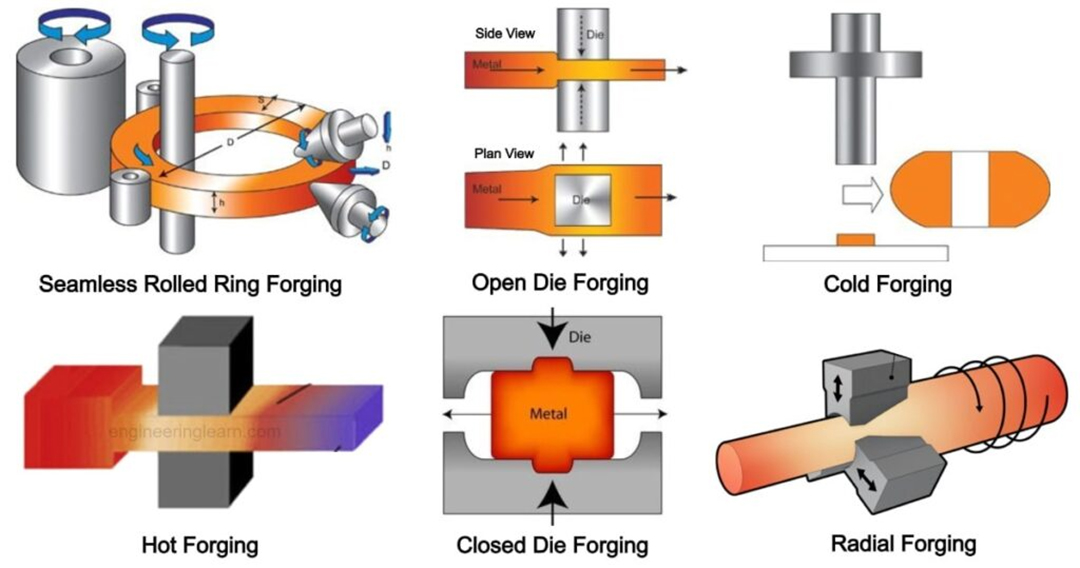
Forging Types
Forging is a metal forming process in which a metal material is heated to a plastic state and force is applied to deform it into the desired shape. According to different classification methods, forging can be divided into different types, the following are some common classification methods:
- According to the state of the metal during the forging process, forging can be divided into the following types:
Cold forging: Cold forging is a metal working technique to process bar stock and squeeze it into an open die. This method occurs atambient temperature or below the metal's recrystallization temperature to form the metal into the desired shape.
Hot forging: Heating metal materials to a certain temperature to make them more plastic, and then performing hammering, extrusion and other processing.
Warm forging: Between cold forging and hot forging, the metal material is heated to a lower temperature to make it easier to be plasticized, and then hammered, extruded and other processes are performed.

- According to different forging processes, forging can be divided into the following types:
Free forging: also known as free hammer forging, is a method of hammering and extruding metal through the free fall of the hammer head on the forging machine.
Die forging: A method of forming a metal material by pressing it into a die using a specific metal die.
Precision forging: a forging method for manufacturing parts with high precision and high quality requirements.
Plastic forming: Including rolling, stretching, stamping, deep drawing and other forming methods, it is also considered as a forging method.
- According to the different forging materials, forging can be divided into the following types:
Brass forging: refers to various forging processes on brass and its alloys.
Aluminum alloy forging: refers to various forging processes for aluminum and its alloys.
Titanium alloy forging: refers to various forging processes for titanium and its alloys.
Stainless steel forging: refers to various forging processes for stainless steel and its alloys.
- According to the different forging shapes, forging can be divided into the following types:
Flat forging: pressing metal materials into a flat shape according to a certain thickness and width.
Cone Forging: Pressing a metal material into a conical shape.
Bending forging: forming the metal material into the desired shape by bending.
Ring forging: Forging a metal material into a ring shape.
- According to the different forging pressure, forging can be divided into the following types:
Stamping: The working of metal under low pressure, usually suitable for the production of thinner metal parts.
Medium-pressure forging: Requires greater pressure than stamping and is usually suitable for producing parts of medium thickness.
High Pressure Forging: Forging requires a lot of pressure and is usually suitable for producing thicker parts.
- According to different forging applications, forging can be divided into the following types:
Auto parts forging: Manufacture various parts that need to be used in cars, such as engine parts, chassis parts, etc.
Aerospace forging: parts required for manufacturing aircraft, rockets and other aerospace devices.
Energy Forging: Manufacture parts needed in various energy equipment, such as boilers, gas turbines, etc.
Mechanical forging: Manufacture parts that need to be used in various mechanical equipment, such as bearings, gears, connecting rods, etc.
1. Improved strength and durability: Forging can improve the mechanical properties of metal, making it stronger and more durable.
2. Precision shaping: Forging allows for precision shaping of metal, which is important in manufacturing parts with specific shapes and sizes.
3. Enhanced material properties: The forging process can improve the material properties of metal, such as corrosion resistance and wear resistance, making it more suitable for demanding applications.
4. Reduced waste: Compared to other metalworking processes, forging generates less waste and allows for better material utilization, which can help reduce costs.
5. Improved surface finish: Forging can result in a smooth surface finish, which is important for parts that need to fit together or slide against each other.
6. Increased production efficiency: With advances in forging technology, the process has become faster and more efficient, allowing for increased production output.

